Single-Cell RNA Sequencing of the Cynomolgus Macaque Testis Reveals Conserved Transcriptional Profiles during Mammalian Spermatogenesis
Lau X, Munusamy P, Ng MJ, Sangrithi M, 13.08.2020
Abstract
Spermatogenesis is highly orchestrated and involves the differentiation of diploid spermatogonia into haploid sperm. The process is driven by spermatogonial stem cells (SSCs). SSCs undergo mitotic self-renewal, whereas sub-populations undergo differentiation and later gain competence to initiate meiosis. Here, we describe a high-resolution single-cell RNA-seq atlas of cells derived from Cynomolgus macaque testis. We identify gene signatures that define spermatogonial populations and explore self-renewal versus differentiation dynamics. We detail transcriptional changes occurring over the entire process of spermatogenesis and highlight the concerted activity of DNA damage response (DDR) pathway genes, which have dual roles in maintaining genomic integrity and effecting meiotic sex chromosome inactivation (MSCI). We show remarkable similarities and differences in gene expression during spermatogenesis with two other eutherian mammals, i.e., mouse and humans. Sex chromosome expression in the male germline in all three species demonstrates conserved features of MSCI but divergent multicopy and ampliconic gene content.
Lau X, Munusamy P, Ng MJ, Sangrithi M. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing of the Cynomolgus Macaque Testis Reveals Conserved Transcriptional Profiles during Mammalian Spermatogenesis. Dev Cell. 2020 Aug 24;54(4):548-566.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.07.018. Epub 2020 Aug 13. PMID: 32795394.
Publication: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2020.07.018
 Disclaimer
Disclaimer
The publication Single-Cell RNA Sequencing of the Cynomolgus Macaque Testis Reveals Conserved Transcriptional Profiles during Mammalian Spermatogenesis by Lau X, Munusamy P, Ng MJ, Sangrithi M is published under an open access license: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/. Permits non-commercial re-use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Curation by the MFGA team Relevant data sets presented in the publication have been identified. If possible, annotations (title, general information, conditions, processed tissue types and processed cell types) have been added based on information from the publication. Data tables and images that provide a good overview on the publication's findings on the data set have been extracted from the publication and/or supplement. If not stated otherwise, images are depicted with title and description exactly as in the publication. Tables have been adjusted to the MFGA table format. Conducted adjustments are explained in the detailed view of the tables. However, titles and descriptions have been adopted from the publication.
Data set 1: scRNA-seq establishes germ and somatic cell types sesiding within the cynomolgus testis
Transcriptome: Single-cell RNA-Sequencing
Species
| Species |
|---|
| Cynomolgus Macaque |
Tissue Types
| BRENDA tissue ontology | Maturity | Description | Species | Replicates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BTO_0001363: testis | 1 infant, 1 juvenile, 2 adults | A typically paired male reproductive gland that produces sperm and that in most mammals is contained within the scrotum at sexual maturity. | Cynomolgus Macaque | 4 |
Images
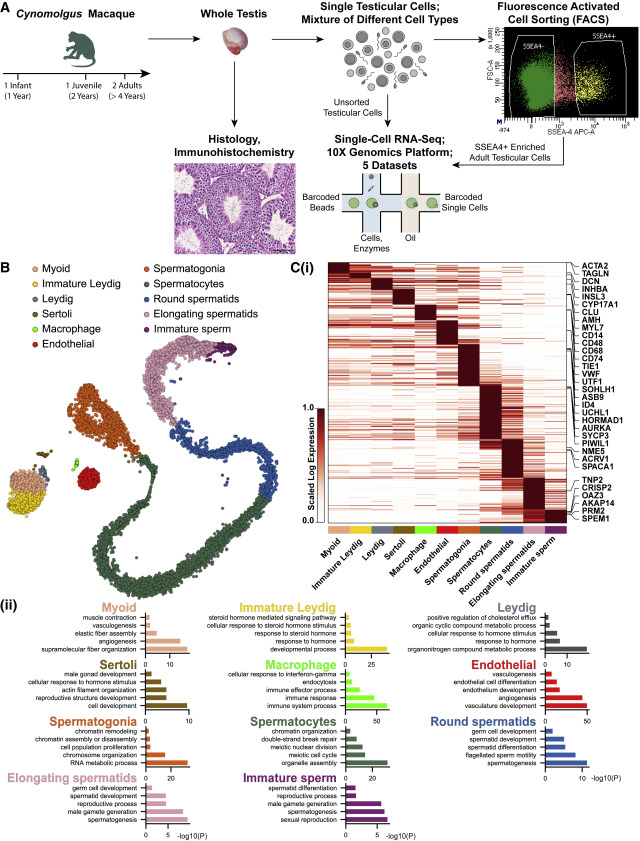
Figure 1: Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Establishes Germ and Somatic Cell Types Residing within the Cynomolgus Testis
(A) Schematic of the experimental design. (B) t-SNE of scRNA-seq data comprising 16,932 cells (cells are colored by the 11 broad cell types). (C) (Ci) Heatmap showing expression of differentially expressed genes for the main cell types. Horizontal ribbons depict the identified cell types. (Cii) Representative GO terms and p values are shown for each cell type.
Licensed under: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
Data set 2: Spermatogonial differentiation
Transcriptome: Single-cell RNA-Sequencing
Species
| Species |
|---|
| Cynomolgus Macaque |
Tissue Types
| BRENDA tissue ontology | Maturity | Description | Species | Replicates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BTO_0001363: testis | 1 infant, 1 juvenile, 2 adults | A typically paired male reproductive gland that produces sperm and that in most mammals is contained within the scrotum at sexual maturity. | Cynomolgus Macaque | 4 |
Images
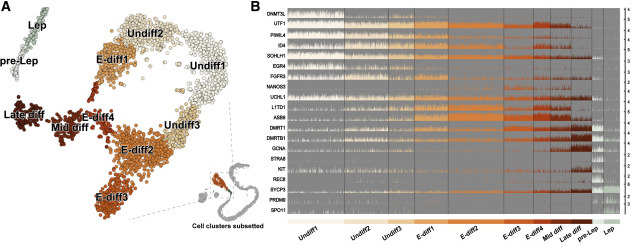
Figure 2: Spermatogonial Differentiation
(A) t-SNE of 3,060 spermatogonial cells and colored by cell clusters. (B) A tracks-based bar-plot depicting the expression levels of key genes involved during spermatogonial differentiation are shown at a single-cell level (upper limits for y axis differ for each track).
Licensed under: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
Data set 3: Integrated Analysis of Spermatogenesis in Three Eutherian Mammals
Transcriptome: Single-cell RNA-Sequencing
Species
| Species |
|---|
| Cynomolgus Macaque |
Tissue Types
| BRENDA tissue ontology | Maturity | Description | Species | Replicates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BTO_0001363: testis | A typically paired male reproductive gland that produces sperm and that in most mammals is contained within the scrotum at sexual maturity. | Cynomolgus Macaque |
Images
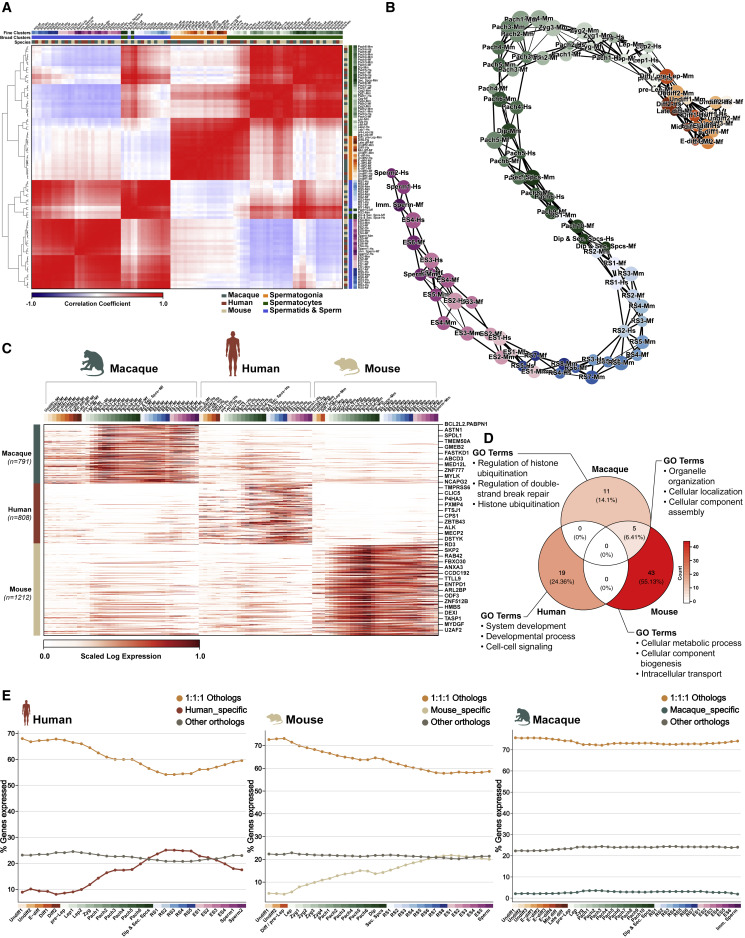
Figure 3: Integrated Analysis of Spermatogenesis in Three Eutherian Mammals
(A) Correlation analysis and hierarchical clustering of germ cell clusters across three species (i.e., cynomolgus, mouse, and human). (B) PAGA graph of cluster relationships on the integrated dataset. Colors of clusters representing similar cell types have been kept the same across the three species. (C) Heatmap of differentially expressed gene orthologs between the three species. (D) Venn diagram of GO terms for genes depicted in (C). (E) Line plot depicting the percentage of gene classes that are expressed in each species over the course of spermatogenesis, i.e., 1-1-1 orthologous genes (orange), other orthologs (in gray), and species-specific genes (specific colors as shown).
Licensed under: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
Data set 4: Transcription factor activity during spermatogenesis
Transcriptome: Single-cell RNA-Sequencing
Species
| Species |
|---|
| Cynomolgus Macaque |
Tissue Types
| BRENDA tissue ontology | Maturity | Description | Species | Replicates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BTO_0001363: testis | A typically paired male reproductive gland that produces sperm and that in most mammals is contained within the scrotum at sexual maturity. | Cynomolgus Macaque |
Images
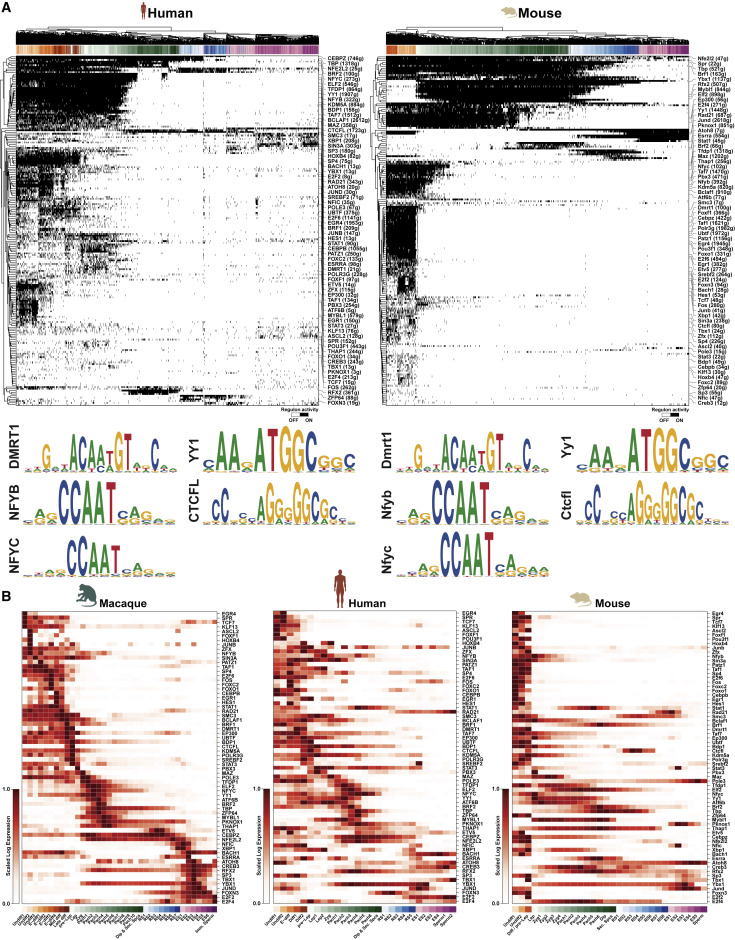
Figure 4: SCENIC Analysis of Regulon Activity and Transcription Factors in Meiosis
(A) Binary plots depicting active regulons in single cells from the mouse and human datasets; regulons and cells are ordered by hierarchical clustering. 68 regulons active in both species are shown. Representative TF motifs are depicted. Color legends refer to clusters described in Figure S5. (B) Heatmaps of TF expression in cynomolgus, human, and the mouse respectively, identified in SCENIC analysis mentioned above. (cynomolgus orthologous for TAF7 and POU3F1 were not identified).
Licensed under: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
