High-resolution analysis of germ cells from men with sex chromosomal aneuploidies reveals normal transcriptome but impaired imprinting
Sandra Laurentino, Laura Heckmann, Sara Di Persio, Xiaolin Li, Gerd Meyer zu Hörste, Joachim Wistuba, Jann-Frederik Cremers, Jörg Gromoll, Sabine Kliesch, Stefan Schlatt and Nina Neuhaus, 28.08.2019
Abstract
Background: The most common sex chromosomal aneuploidy in males is Klinefelter syndrome, which is characterized by at least one supernumerary X chromosome. While these men have long been considered infertile, focal spermatogenesis can be observed in some patients, and sperm can be surgically retrieved and used for artificial reproductive techniques. Although these gametes can be used for fertility treatments, little is known about the molecular biology of the germline in Klinefelter men. Specifically, it is unclear if germ cells in Klinefelter syndrome correctly establish the androgenetic DNA methylation profile and transcriptome. This is due to the low number of germ cells in the Klinefelter testes available for analysis. Results: Here, we overcame these difficulties and successfully investigated the epigenetic and transcriptional profiles of germ cells in Klinefelter patients employing deep bisulfite sequencing and single-cell RNA sequencing. On the transcriptional level, the germ cells from Klinefelter men clustered together with the differentiation stages of normal spermatogenesis. Klinefelter germ cells showed a normal DNA methylation profile of selected germ cell-specific markers compared with spermatogonia and sperm from men with normal spermatogenesis. However, germ cells from Klinefelter patients showed variations in the DNA methylation of imprinted regions. Conclusions: These data indicate that Klinefelter germ cells have a normal transcriptome but might present aberrant imprinting, showing impairment in germ cell development that goes beyond mere germ cell loss. Keywords: Deep bisulfite sequencing, DNA methylation, Klinefelter syndrome, Male germline, Sex chromosome aneuploidy, Single-cell analysis, Sperm, Spermatogonia.
LAURENTINO, Sandra, et al. High-resolution analysis of germ cells from men with sex chromosomal aneuploidies reveals normal transcriptome but impaired imprinting. Clinical epigenetics, 2019, 11. Jg., Nr. 1, S. 127.
Publication: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-019-0720-3 Repository: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE130151
 Disclaimer
Disclaimer
The publication High-resolution analysis of germ cells from men with sex chromosomal aneuploidies reveals normal transcriptome but impaired imprinting by Sandra Laurentino, Laura Heckmann, Sara Di Persio, Xiaolin Li, Gerd Meyer zu Hörste, Joachim Wistuba, Jann-Frederik Cremers, Jörg Gromoll, Sabine Kliesch, Stefan Schlatt and Nina Neuhaus is published under an open access license: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. Permits to share, copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format and to adapt, remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
Curation by the MFGA team Relevant data sets presented in the publication have been identified. If possible, annotations (title, general information, conditions, processed tissue types and processed cell types) have been added based on information from the publication. Data tables and images that provide a good overview on the publication's findings on the data set have been extracted from the publication and/or supplement. If not stated otherwise, images are depicted with title and description exactly as in the publication. Tables have been adjusted to the MFGA table format. Conducted adjustments are explained in the detailed view of the tables. However, titles and descriptions have been adopted from the publication.
Data set 1: Single-cell RNA-Sequencing from Klinefelter testicular tissue
Transcriptome: Single-cell RNA-Sequencing
Species
| Species |
|---|
| Human |
Conditions
| Human phenotype ontology | Participants | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| HP:klinefelter: Klinefelter Syndrome | 1 |
Tissue Types
| BRENDA tissue ontology | Maturity | Description | Species | Replicates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BTO_0001363: testis | Adult | 3289 testicular cells | Human | 1 |
Cell Types
| Cell ontology | Maturity | Description | Species | Replicates | Cells per replicate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL_0000115: endothelial cell | Adult | Human | 1 | ||
| CL_0002481: peritubular myoid cell | Adult | Human | 1 | ||
| CL_0000178: Leydig cell | Adult | Human | 1 | ||
| CL_0000586: germ cell | Adult | Human | 1 | 39.0 | |
| CL_0000216: Sertoli cell | Adult | Human | 1 | ||
| CL_0000235: macrophage | Adult | Human | 1 |
Images
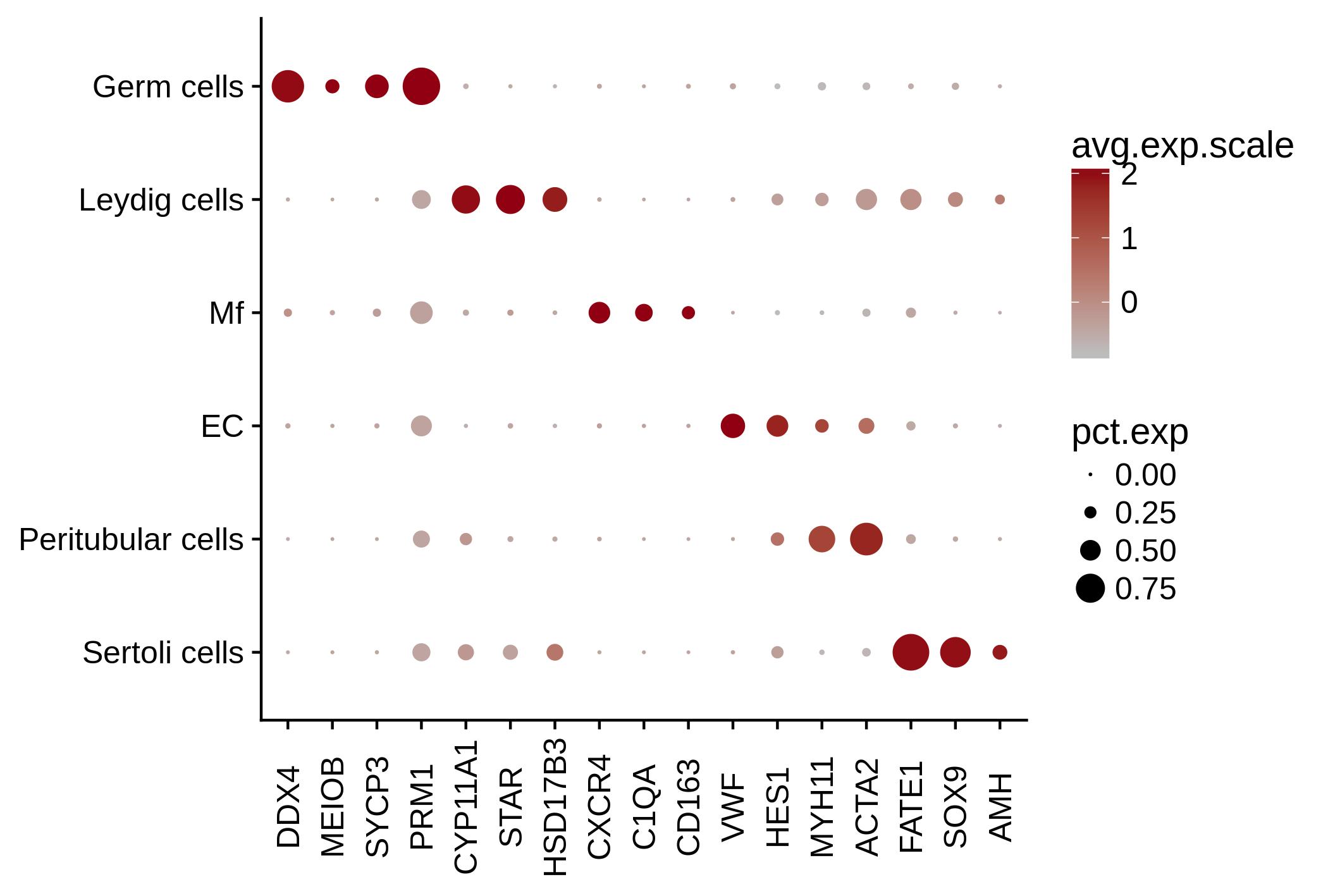
Figure 2B: Testicular cell marker genes
Expression profiles of specific testicular cell marker genes in the different cell clusters identified in marker-based clustering.
Licensed under: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
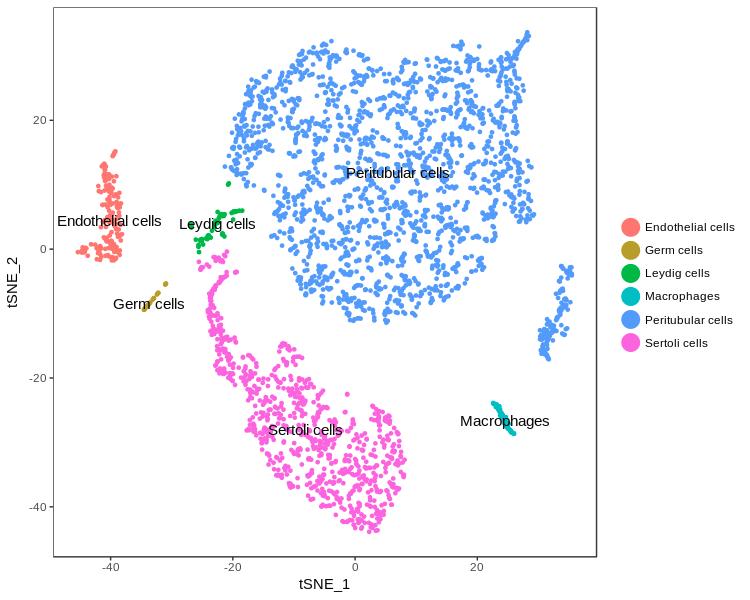
Figure 2A: Marker-based clustering
t-SNE plot showing the clustering of the different testicular cell types present in a Klinefelter sample.
Licensed under: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
Data set 2: DNA methylation analysis of germ and somatic cell fractions in normal and Klinefelter patients.
Methylome: Targeted Deep Bisulfite Sequencing
Species
| Species |
|---|
| Human |
Conditions
| Human phenotype ontology | Participants | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| HP:control | 5 | |
| HP:klinefelter: Klinefelter Syndrome | 7 | 4 Klinefelter syndrome with testicular germ cells & 3 Klinefelter syndrome without testicular germ cells (Sertoli cell only syndrome) |
Tissue Types
| BRENDA tissue ontology | Maturity | Description | Species | Replicates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BTO_0000089: blood | Adult | Klinefelter | Human | 6 |
| Adult | Somatic enriched fraction from Klinefelter | Human | 6 | |
| Adult | Germ cell enriched fraction from Klinefelter | Human | 3 | |
| Adult | Somatic enriched fraction from normal | Human | 5 | |
| Adult | Germ cell enriched fraction normal | Human | 4 | |
| BTO_0000089: blood | Adult | normal | Human | 3 |
Cell Types
| Cell ontology | Maturity | Description | Species | Replicates | Cells per replicate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL_0000019: sperm | Adult | normal | Human | 6 |
Images
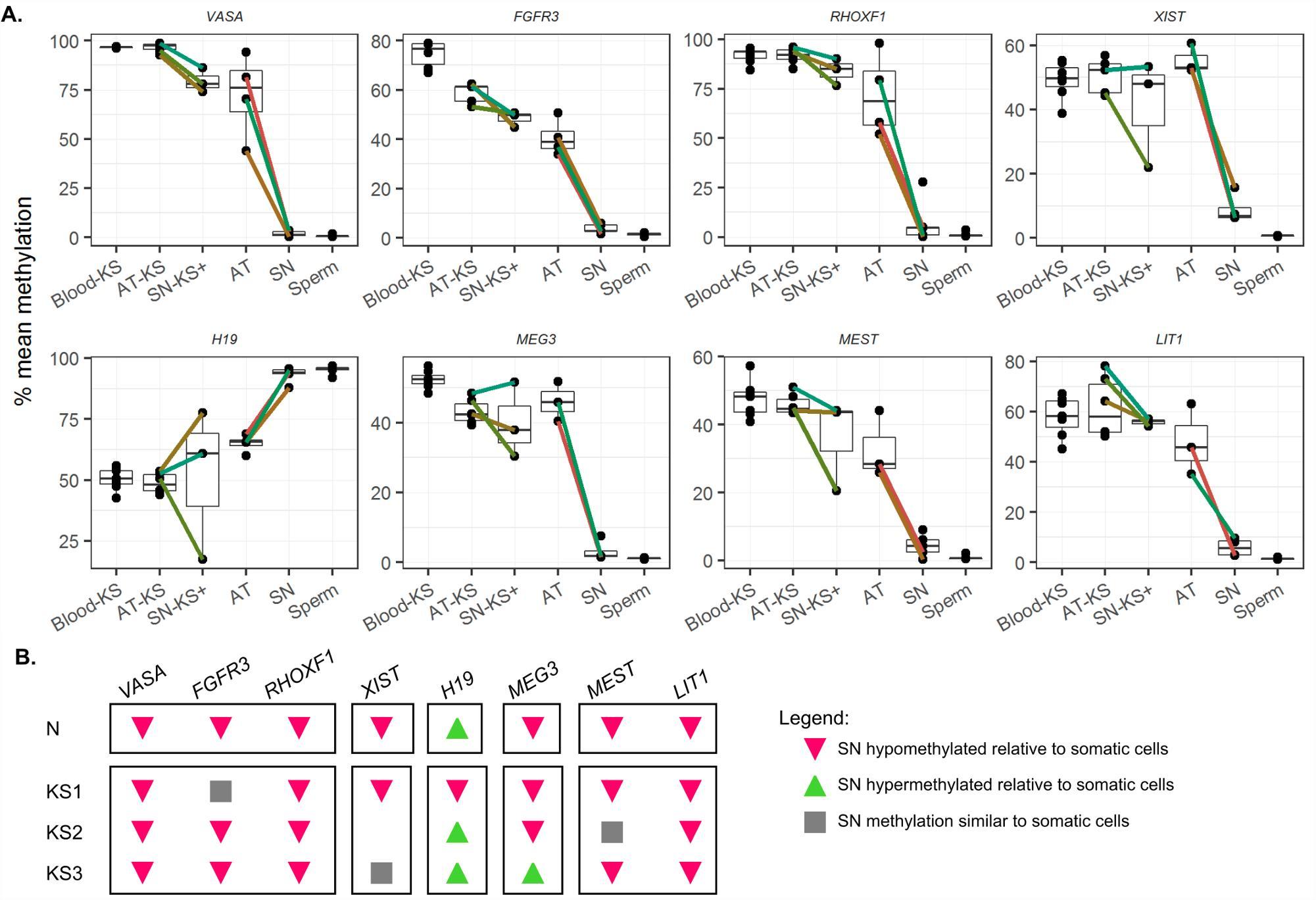
Figure 5A: DNA methylation in germ (SN) and somatic cell (AT) fractions in normal and Klinefelter patients.
a) Samples obtained from the same individual are connected by individually coloured lines. b) Summary of the pattern of DNA differences between somatic and germ cells. Only a representative pattern is shown for normal samples due to the homogeneity of the patterns. Blood-KS blood from Klinefelter syndrome patients, AT-KS somatic cell fraction from Klinefelter samples, SN-KS+ germ cell enriched fraction from Klinefelter samples, AT somatic fraction from normal man, SN germ cell fraction from normal man.
Licensed under: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
