Single-cell RNA-seq uncovers dynamic processes and critical regulators in mouse spermatogenesis
Yao Chen, Yuxuan Zheng, Yun Gao, Zhen Lin, Suming Yang, Tongtong Wang, Qiu Wang, Nannan Xie, Rong Hua, Mingxi Liu, Jiahao Sha, Michael D. Griswold, Jinsong Li, Fuchou Tang & Ming-Han Tong, 30.07.2018
Abstract
A systematic interrogation of male germ cells is key to complete understanding of molecular mechanisms governing spermatogenesis and the development of new strategies for infertility therapies and male contraception. Here we develop an approach to purify all types of homogeneous spermatogenic cells by combining transgenic labeling and synchronization of the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium, and subsequent single-cell RNA-sequencing. We reveal extensive and previously uncharacterized dynamic processes and molecular signatures in gene expression, as well as specific patterns of alternative splicing, and novel regulators for specific stages of male germ cell development. Our transcriptomics analyses led us to discover discriminative markers for isolating round spermatids at specific stages, and different embryo developmental potentials between early and late stage spermatids, providing evidence that maturation of round spermatids impacts on embryo development. This work provides valuable insights into mammalian spermatogenesis, and a comprehensive resource for future studies towards the complete elucidation of gametogenesis.
CHEN, Yao, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq uncovers dynamic processes and critical regulators in mouse spermatogenesis. Cell research, 2018, 28. Jg., Nr. 9, S. 879.
Publication: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-018-0074-y Repository: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE107644
 Disclaimer
Disclaimer
The publication Single-cell RNA-seq uncovers dynamic processes and critical regulators in mouse spermatogenesis by Yao Chen, Yuxuan Zheng, Yun Gao, Zhen Lin, Suming Yang, Tongtong Wang, Qiu Wang, Nannan Xie, Rong Hua, Mingxi Liu, Jiahao Sha, Michael D. Griswold, Jinsong Li, Fuchou Tang & Ming-Han Tong is published under an open access license: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. Permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as appropriate credit is given to the original author(s) and the source, a link to the Creative Commons license is provided, and changes are indicated.
Curation by the MFGA team Relevant data sets presented in the publication have been identified. If possible, annotations (title, general information, conditions, processed tissue types and processed cell types) have been added based on information from the publication. Data tables and images that provide a good overview on the publication's findings on the data set have been extracted from the publication and/or supplement. If not stated otherwise, images are depicted with title and description exactly as in the publication. Tables have been adjusted to the MFGA table format. Conducted adjustments are explained in the detailed view of the tables. However, titles and descriptions have been adopted from the publication.
Data set 1: A comprehensive transcriptome landscape of mouse mitotic, meiotic, and postmeiotic cells
Transcriptome: Single-cell RNA-Sequencing
Species
| Species |
|---|
| Mouse |
Tissue Types
| BRENDA tissue ontology | Maturity | Description | Species | Replicates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BTO_0001363: testis | Adult | Mouse |
Cell Types
| Cell ontology | Maturity | Description | Species | Replicates | Cells per replicate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL_0000020: spermatogonium | Adult | type A1 and B | Mouse | ||
| CL_0000017: spermatocyte | Adult | preleptotene, leptotene, diplotene, zygotene | Mouse | ||
| CL_0000018: spermatid | Adult | pre-round, round-early and late stage | Mouse | ||
| CL_0000019: sperm | Adult | Mouse |
Images
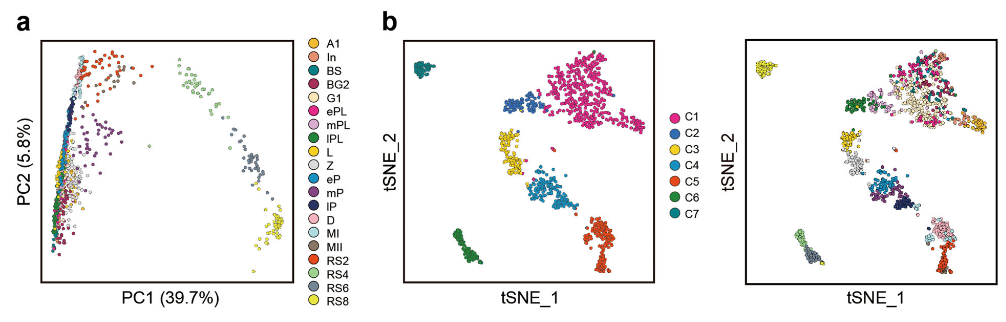
Figure 3 A and B: Characterization of dynamic gene expression patterns in male germ cell development
A: Principal component analysis (PCA) of the spermatogenic cells at 20 different stages based on their gene expression pattern exhibited by PC1 and PC2. The variation values of PC1 and PC2 are 39.7 and 5.8%, respectively. Distinct cell types are shown in different colors.</br>B: The t-distribute stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE) plot with seven clusters of spermatogenic cells (left panel) and their corresponding developmental stages (right panel). Clusters C1 to C7 are shown in different colors. Cells at different developmental stages are shown in different colors as in A.
Licensed under: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
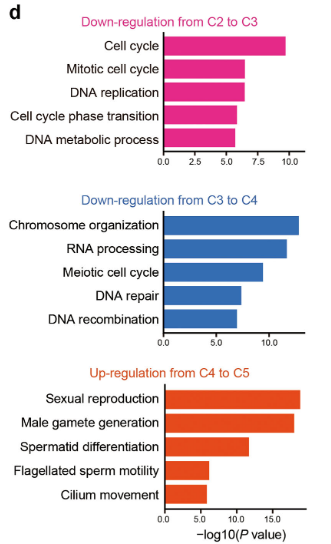
Figure 3 D: Characterization of dynamic gene expression patterns in male germ cell development
Gene ontology (GO) analysis of downregulated DEGs from clusters C2 to C3 (upper panel), down-regulated DEGs from C3 to C4 (middle panel) and up-regulated DEGs from C4 to C5 (bottom panel), respectively. The dynamic gene expression patterns of these three groups are shown in c
Licensed under: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
Results
- Table S2: Clustering results of cells in twenty developmental stages. first
- Table S3.1-6: Differentially expressed genes between consecutive clusters, Related to Figure 3 first
- Table S3.7-19: Differentially expressed genes between consecutive stages, Related to Figure 3 first
- Table S6: Differentially expressed genes between Sox30-cKO and wild-type round spermatids. first
- Table S8.1: Sex-linked protein-coding gene expression during spermatogenesis, Related to Figure 7 first
- Table S4.1: A1 to In (down-regulation) first
- Table S4.2: In to BS (up-regulated) first
- Table S4.3: BS to BG2 (up-regulation) first
- Table S4.4: BG2 to G1 (down-regulation) first
- Table S4.5: G1 to ePL (up-regulation) first
- Table S8.2 MSCI-related genes during spermatogenesis, Related to Figure 7 first
Data set 2: Alternative splicing genes and differentially expressed splicing factors during mouse spermatogenesis
Transcriptome: Single-cell RNA-Sequencing
Species
| Species |
|---|
| Mouse |
Tissue Types
| BRENDA tissue ontology | Maturity | Description | Species | Replicates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BTO_0001363: testis | Adult | Mouse |
Cell Types
| Cell ontology | Maturity | Description | Species | Replicates | Cells per replicate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL_0000020: spermatogonium | Adult | type A and B | Mouse | ||
| CL_0000017: spermatocyte | Adult | preleptotene, leptotene, diplotene, zygotene | Mouse | ||
| CL_0000018: spermatid | Adult | pre-round, round-early and late stage | Mouse | ||
| CL_0000019: sperm | Adult | Mouse |
Images
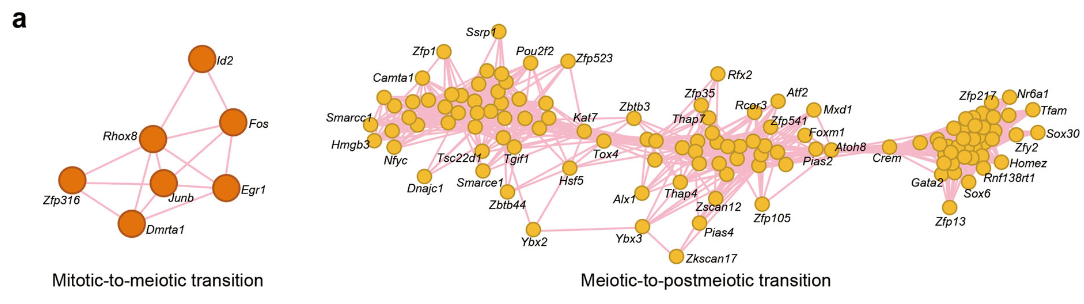
Figure 5 A: Transcriptional regulation in mouse spermatogenesis
Gene regulation network analysis of mitotic-to-meiotic transition (left panel) and meiotic-to-postmeiotic transition (right panel). Edges indicate interactions between transcriptional factors (TFs). Circles indicate the TFs.Only TFs with high correlation and at least three edges are shown.
Licensed under: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
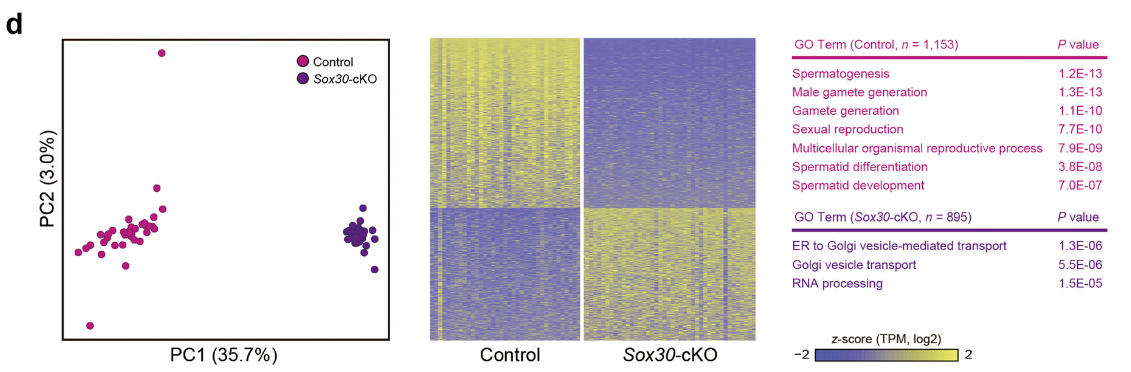
Figure 5 D: Principal component analysis (PCA) (left panel) of steps 3–4 spermatids inSox30-cKO and wild-type control mice
The cells fromSox30-cKO mice are shown in purple, whereas cells from wild-type mice are in fuchsia. The variation values of PC1 and PC2 are 35.7% and 3.0%, respectively.Heatmap (middle panel) showing the distinct gene expression characteristics between spermatogenic cells ofSox30-cKO and wild-typecontrol mice. Color key from yellow to blue represents the relative gene expression level from high to low. GO analysis (right panel) indicates the potential functions of DEGs inwild-type (fuchsia) andSox30-cKO mice (purple).
Licensed under: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
